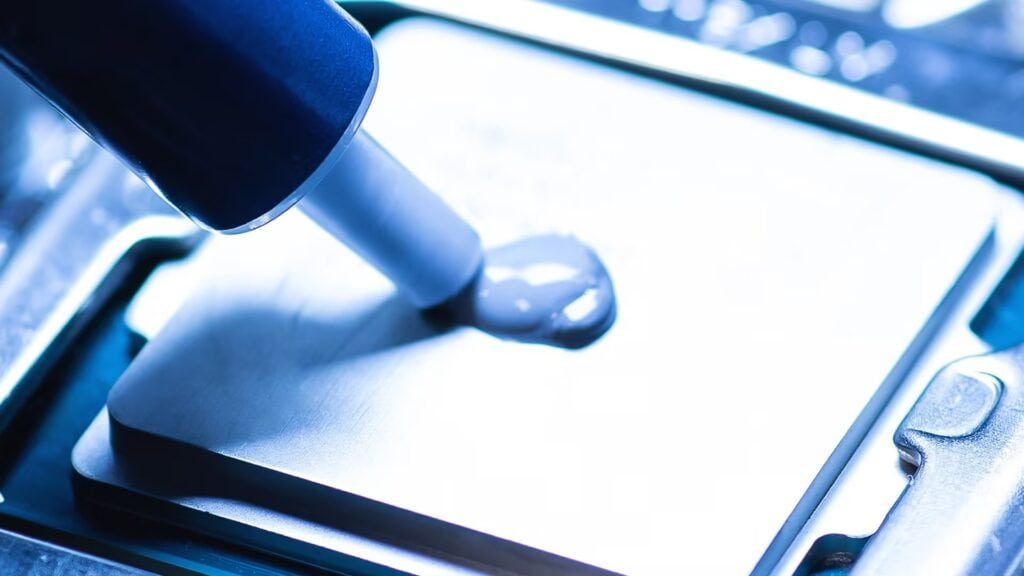
Heat management is something very important in modern electronics. For example, devices are getting smaller and more powerful, they generate more heat in tight spaces. This extra heat can slow down devices and make them break down faster. Thermally conductive glue helps solve this problem. It’s a special adhesive that moves heat away from hot components. The glue fills tiny gaps and creates better contact between parts. This helps keep electronics cool and working properly.
Understanding Thermally Conductive Glue
Definition and Basic Composition
Thermally conductive glue is a special type of adhesive. It does two jobs at once. It bonds materials together and transfers heat. The glue has two main parts. First is the binder matrix, which acts as the base adhesive. Second are the thermally conductive fillers. The binder creates the sticky properties. The fillers help move heat through the material. These fillers are made from special materials. They include silver, graphite, or ceramic particles. Each filler is chosen for how well it conducts heat.
Main Components and Their Roles
The binder matrix is the foundation of the glue. It can be made from several materials. These include epoxy, silicone, polyurethane, or acrylic. Each type has different features. Some are more flexible. Others take different times to dry.
The bonding strength also varies. The thermally conductive fillers are mixed into this base. These particles create paths for heat to move. More fillers mean better heat transfer. The type of filler affects performance. The mix of components is carefully chosen for each use.
Types of Thermally Conductive Adhesives
Epoxy-based adhesives are very strong. They resist chemical damage well. They come in one-part or two-part systems. Their heat transfer is excellent. But they take longer to dry fully. Silicone-based options stay flexible after drying. They work well in high heat. They’re waterproof too. Adhesives can join different types of materials.
Polyurethane adhesives work on many surfaces. They come in one-part or two-part options. Some types keep water out. Acrylic adhesives dry quickly. They form strong bonds. They resist chemicals well.
Special Forms and Alternatives
These materials also come as films and tapes. These are pre-made sheets. You can cut them to exact sizes. They have the same thickness everywhere. This makes assembly faster. They provide consistent results.
Thermal grease is different from these adhesives. It doesn’t create bonds. It only fills air gaps. It’s mainly used between heat sinks and processors. Thermal grease helps transfer heat but won’t hold parts together.
Mechanisms of Heat Dissipation Improvement
Heat’s got to move, right? It’s like people leaving a concert after the show. They all want to get out. Heat is the same. It goes from hot spots to cooler spots. That’s just how heat rolls. We call this thermal conduction. It’s the main way heat gets out of your electronics. Think of it as heat naturally wanting to spread out and find some space.
Role of Thermally Conductive Glue in Enhancing Conduction:
This glue? It’s a game changer for heat. It’s not magic, but it’s close. It helps heat move in a few key ways. Simple stuff, but it makes a huge difference.
Increasing Contact Surface Area:
If you just barely touch fingertips, it’s not much of a connection. But if you grab their whole hand, that’s a solid connection. Same with heat. When you stick a hot chip to a heat sink, they don’t really touch everywhere. Tiny air gaps are always there. Air? Air blocks heat. This glue? It fills those gaps. It’s like filling in the cracks in that handshake, making it a full, strong grip. More contact area means heat flows way better. Just like that solid handshake passes the warmth.
Reducing Thermal Resistance:
Think about running through mud. Hard, right? That mud is like resistance. It slows you down. Heat faces resistance too when it tries to move from one thing to another. This glue? It’s like paving the muddy path. It lowers the resistance. Makes it way easier for heat to flow from the hot chip to the heat sink. Less resistance, more heat gets through, simple as that.
Improving Thermal Pathways:
Imagine you’re in a crowded room and need to get to the exit. If there are clear paths, you’re out fast. If it’s a mess of furniture and people, it’s slow and annoying. Heat is the same. It wants clear paths to escape. This glue? It creates those clear paths. It’s like building highways for heat to zoom away from the hot parts and into the heat sink, which is like a big open space for heat to spread out and chill. Good pathways are key.
Bond Line Thickness Importance:
Now, don’t go overboard with the glue. Think of putting on a sweater. One sweater? Good warmth. Ten sweaters? You’ll overheat! Too much glue is like too many sweaters for heat. A thin layer of this glue is usually best. It’s like a thin, strong bridge is faster to cross than a giant, thick one. You want enough glue to make a good connection, but keep it thin so heat can zoom through. It’s a balance.
Heat Dissipation Paths in Electronic Devices:
So, where does heat go in your gadgets? Few routes.
- Conduction through components and PCB: Heat travels through the solid parts. Like walking through hallways in a building. This is the main route.
- Convection from package surfaces: Heat rises off the surface. Like feeling the warmth from a hot coffee cup.
- Radiation (less significant in small electronics): Everything gives off a little heat as radiation. Like feeling the sun, but way less strong in your phone.
This thermally conductive glue? It’s mostly about that first one, conduction. Making sure heat can zoom through the connection and get to where it needs to go. Keeps things cool. Keeps things running right.
4. Advantages of Using Thermally Conductive Glue
Enhanced Thermal Management:
First off, it’s all about keeping things cool, right? That’s what this glue is for. Thermal management ensures that heat moves away so well, your gadgets just work better. They don’t get all sluggish and slow when they’re hot. Think of it like running a marathon – you perform way better when you’re not overheating.
This glue helps electronics run their marathon without breaking a sweat. It’s all about effective heat transfer leading to optimal thermal performance. Plus, it stops things from going totally haywire and burning out from too much heat – no overheating or thermal runaway disasters. It just keeps everything at a nice, even temperature. Stable operating temperatures for the win.
Structural Integrity and Bonding:
But it’s not just a heat-mover, this glue is also strong. Like, really strong. It’s not just taping things together. It makes a strong and permanent bond between parts, like your chip and that heat sink we talked about. And get this – sometimes, you don’t even need screws or clips anymore!
This glue can replace those clunky mechanical fasteners. 1 Less fuss, less parts. And because it’s glued solid, things are way more reliable. They can handle bumps and shakes better. Improved reliability and vibration resistance? Yes, please.
Simplified Assembly and Manufacturing:
Building stuff with this glue? Way easier. It’s like switching from building with LEGO bricks to using super-powered sticky tape. Things just go together faster. Faster and more efficient assembly processes. And get this – robots can even use this glue! Think about machines squirting out glue in just the right spot. Automated application possible.
Liquid glue, film glue – all kinds. Plus, you can ditch some of those heavy metal bits and bobs. Reduced component weight and complexity. And if you’ve got weirdly shaped parts? No problem for glue, especially those film types. Suitable for complex geometries. Manufacturing just got a whole lot simpler.
Versatility and Material Compatibility:
This glue isn’t picky. It’s like that friend who gets along with everyone. It sticks to all sorts of stuff. Adhesion to various substrates. Metals, plastics, ceramics, even if they’re different materials. No problem. And they make different kinds of this glue, like different flavors of ice cream. Different chemistries for different jobs.
Need glue that dries super fast? Got it. Need glue that’s extra thick? Got that too. They can even tweak the recipe to get it just right. Customizable formulations are the name of the game. Viscosity, cure time, how well it conducts heat – they can adjust it all.
Electrical Insulation (in some formulations):
Here’s a cool trick. Some of this glue can move heat like a champ, but not electricity. It’s like a one-way street for energy. Thermally conductive but electrically insulating options available. They do this by adding stuff like ceramic or mineral fillers. Why is this cool? Because you can stick hot parts down without worrying about short circuits. Keeps things safe. Important for preventing short circuits and ensuring electrical safety.
Environmental and Chemical Resistance:
And last but not least, this glue is tough. Like, stands-up-to-the-elements tough. It can handle getting a bit wet, or being around chemicals. Protection against moisture, chemicals, and harsh environments. And for really sensitive gadgets, they even make special glue that doesn’t release nasty fumes. Low outgassing formulations for sensitive electronics. Keeps everything clean and protected.
5. Applications of Thermally Conductive Glue
Electronics Industry
This is where this glue really shines. Electronics and heat? They’re not friends. This glue is like the peacemaker, keeping things cool and running smoothly in all sorts of gadgets.
Bonding Heat Sinks to CPUs and GPUs:
The CPU and GPU. They get hot, especially when you’re gaming or doing heavy work. Heat sinks are like radiators for computers, pulling heat away. And this glue? It’s the super-strong, heat-loving bond that sticks those heat sinks right onto the chips. Keeps your computers, servers, and fancy electronics from melting down.
LED Lighting:
Those bright LED lights? They get hot too, believe it or not. Heat is the enemy of LEDs, makes them burn out faster and get dimmer. This glue helps pull the heat away from LEDs in light bulbs and displays. Longer lasting, brighter lights? Thank the glue.
Power Electronics:
Anything that deals with serious power – like inverters, rectifiers, transistors – it makes heat. Lots of it. This glue is used to stick these power parts to coolers, keeping them from overheating and failing. Think power supplies, motor controls, all that heavy-duty electrical stuff.
Semiconductor Packaging:
Those tiny, delicate computer chips? They need protection. And they need to stay cool inside their packaging. This glue is used to encapsulate them, like giving them a comfy, heat-conducting blanket. Keeps them safe and cool.
PCB Assembly:
Circuit boards are packed with tiny parts. Some of those parts get hot. This glue helps stick those hot parts to the board, or to little heat spreaders on the board. Also used as a kind of heat-moving “goop” to cover parts on the board and keep them cool.
Automotive Electronics:
Cars are going electric, and electric cars are full of electronics. Batteries in EVs make tons of heat. This glue is used everywhere in EV batteries – sticking battery cells together, sticking them to cooling plates, building the whole battery pack. Also used in car inverters, chargers, and all the other electronics in modern cars. Cars are getting smart and cool, thanks to glue.
Aerospace and Military Devices:
Out in space or in tough military gear? Things have to work, and they have to be reliable. Heat is a killer in these situations. This glue is used in planes, satellites, military equipment – anywhere where things cannot fail and heat needs to be managed perfectly. High stakes, high reliability, glue to the rescue.
Medical Devices:
Hospitals are full of electronics, from scanners to monitors. These devices need to be reliable and safe. Heat management is key. This glue helps keep medical equipment running smoothly and accurately, and keeps patients safe.
Thermally Conductive Glue vs. Alternatives
Adhesion:
Glue sticks. Really sticks. Provides structural bonding. Paste? Just fills gaps. Doesn’t hold things. Like frosting – sits there, not holding cake layers.
Application:
Glue is permanent. Permanent bonding. Once glued, it stays. Paste? For things you might disassemble later. Like computer CPU coolers. Temporary interfaces. Upgrade cooler later? Use paste, not glue.
Thermal Performance:
Paste often excels at pure heat movement. Designed to fill gaps and remove heat, especially from hot CPUs (CPU/GPU cooling). Glue is good at heat too, but also bonds. Paste might be slightly better at heat alone, but glue is still very good and adds strength.
Maintenance:
Paste can dry out. Might need cleaning and fresh paste occasionally (periodic reapplication). Glue? Once set, it’s set. Permanent. No need to redo it.
Typical Use Cases:
Paste is best for CPU coolers, graphics card coolers – top heat transfer, possible part swaps. Glue? Great for permanent heat sink attachment, LEDs, power electronics – strong bond and good heat flow.
Thermally Conductive Glue vs. Thermal Pads:
Thermal pads are like squishy, heat-moving stickers. Thermal cushions.
Conformability:
Glue is liquid-like. Squeezes into all spaces, fill intricate gaps well. Pads? Solid. Good for flat surfaces, less so for uneven ones.
Ease of Application:
Pads are very easy. Peel and stick. Done. Glue? Can be messier, liquid glue especially. More careful glue application needed, especially liquids.
Thermal Performance:
Glue can often provide better heat transfer, lower thermal resistance. Pads are good, consistent thickness is useful. But glue often fills air gaps better, better connection.
Mechanical Stability:
Pads are squishy, absorb vibrations. Vibration suppression is a pad benefit. Glue? Rigid. Strong bond, less squish.
Typical Use Cases:
Pads are good for quick, easy use, maybe vibration damping. Laptops, some consumer electronics, fast assembly needed. Glue? Better when best heat transfer is needed, uneven surfaces, and strong, permanent bond.
Conclusion
Thermally conductive glue is essential for effective heat management in today’s electronics. It improves cooling, adds structural strength, and simplifies production.
For a wide range of thermally conductive adhesives, gels, and pads, consider Jiuju Tech. Our products are perfect for a wide range of applications such as electronics and automotive to industrial uses.