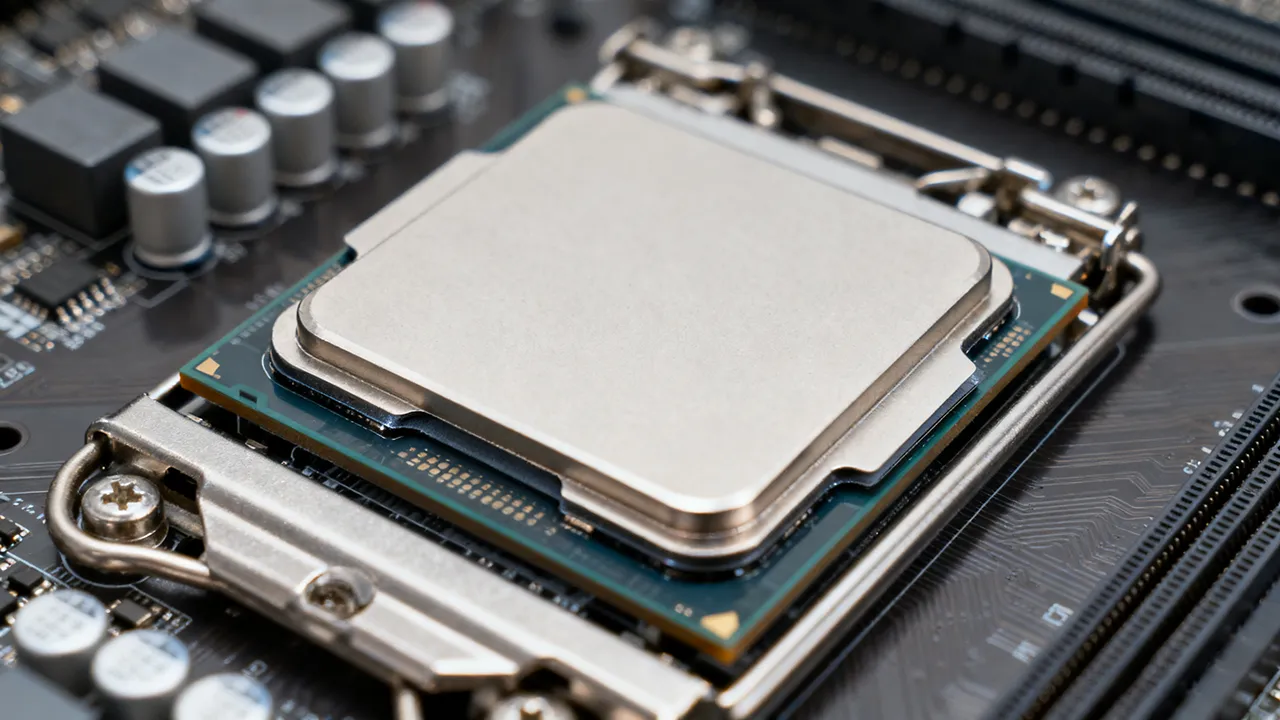
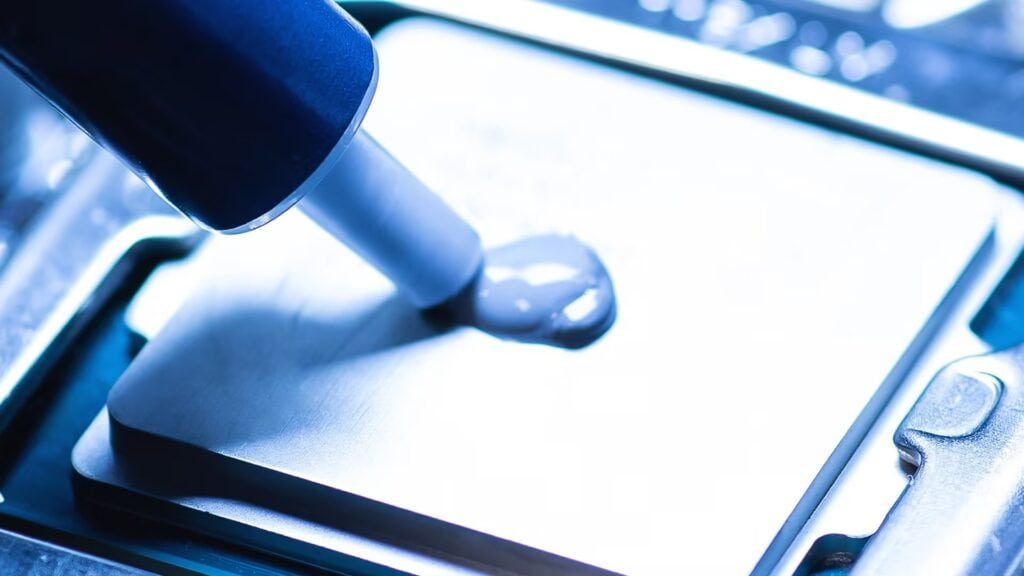
The cooling systems are necessary to avoid overheating of electronic devices, and industrial machines. This is why heat sinks are provided with gaming consoles, power electronics, automotive systems and telecommunication equipment. These elements assist in keeping the temperatures at low levels since they absorb heat to the air.
When a heat sink is applied to an electronic component, there are small air bubbles left between the two surfaces. These vents slow the transfer of heat and significantly worsen the performance of the heatsink. To remove this problem, thermal interface media (TIMs), which could be thermal pads or thermal paste are used.
Thermal interface solutions of high quality enhance the conductivity of heat between surfaces. PTM7950 is one of the popular phase change materials (PCMs) of cooling units among others. Its PCM system in the form of polymer also provides excellent thermal conductivity and thus can be used in various industries.
Then, why is PTM7950 any different and what is its comparison with phase change thermal pads? This article will give you the information to make a better choice regarding the cooling system of its device.
Types of Thermal Interface Materials
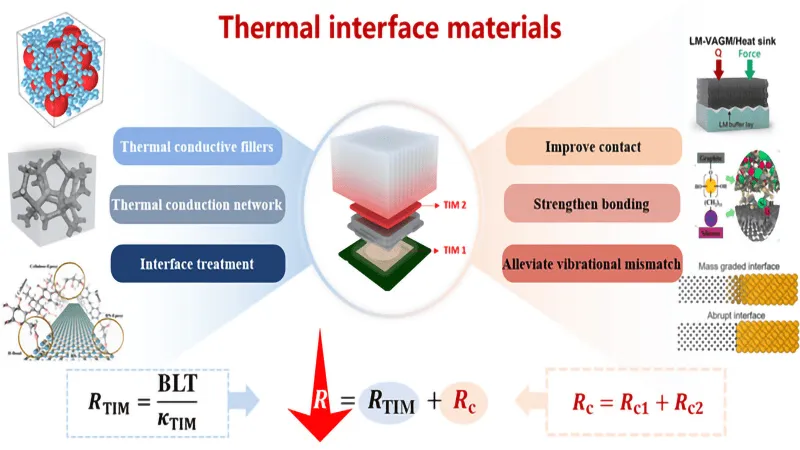
Different thermal interface materials available in the market are divided into two categories: solid and liquid.
Liquid TIMs
Liquid TIMs are further divided into these types:
- Thermal grease
- Liquid adhesive
- Gel
- Liquid gap filler
Thermal pastes are preferred by customers for their higher heat transmission and low cost. Grease is easy to apply by any layman and effectively resolves overheating issues. It ensures a longer lifespan of any computing system or other electronic devices.
Gel is applied as thermal grease and has a loose texture to fill in air gaps. People prefer liquid adhesives for mechanical attachment and heat dissipation. Moreover, liquid gap filler works like solid thermal pads, and is suitable to fill in irregular shapes and surfaces.
Solid TIMs
Solid TIMs are further divided into these types:
- Phase change pad
- Gap filler pads
- Films
- Tape adhesives
A phase change pad is the most advanced heating material you can use between surfaces to fill air gaps and improve heat conductivity. Thermal gap filler pads are best used when large gaps are present between surfaces.
Moreover, films are best used when you require electrical insulation along with thermal conductivity. Tape adhesives help attach two surfaces, enabling better, quicker heat transfer and helping manage normal temperatures.
Factors Behind the Selection of a Suitable Thermal Material

Today, different thermal materials are available in the market and each has its own positives and negatives. Some are easy to use and cost effective, while others are pricey but provide better heat conductivity and lower thermal impedance.
Based on your product specifications and personal preference, you can evaluate any thermal product using the following factors:
Thermal Conductivity
The main reason we use thermal interface materials is to get better heat transfer from the heat-generating component to the heatsink. So when choosing one, make sure it has high thermal conductivity.
Reliability of Manufacturer
Reliability of the manufacturer is another important factor before buying any product. Choosing a low quality thermal paste, tape or pad from a maker will not be worth your money and time. Thus, you must check their reliability to avoid any mishap. Shop from reliable brands like Honeywell for optimal thermal solutions.
User Experience
Before selecting any particular thermal solution for an effective cooling system in your computer or other electronic device, check what other users have experienced. Compare all the different materials and check the pros and cons as told by other consumers. For instance, how well does it perform, cooling time and lifespan.
Other Specifications
Some products come with electrical insulation, while others are electrically conductive. Some materials melt upon heating, while others are already available in liquid form. Certain materials require pressure during application, while others need different instructions to follow. These specifications affect the overall performance as well as the choice of manufacturer. So keep an eye on various factors to make the best choice.
Durability and Lifespan
How fast does a thermal material degrade over time and under conditions like temperature or pressure? Does it maintain its performance in the long run? These questions reflect the durability of the thermal product. So, evaluate durability factors when choosing any solution.
Compatibility Concerns
Is the selected thermal product compatible with your device? What type of surface will the paste or pad be applied to? Will the material fill the gaps effectively? Make sure to ask these questions before making your final selection.
Why is Honeywell PTM7950 so Famous?
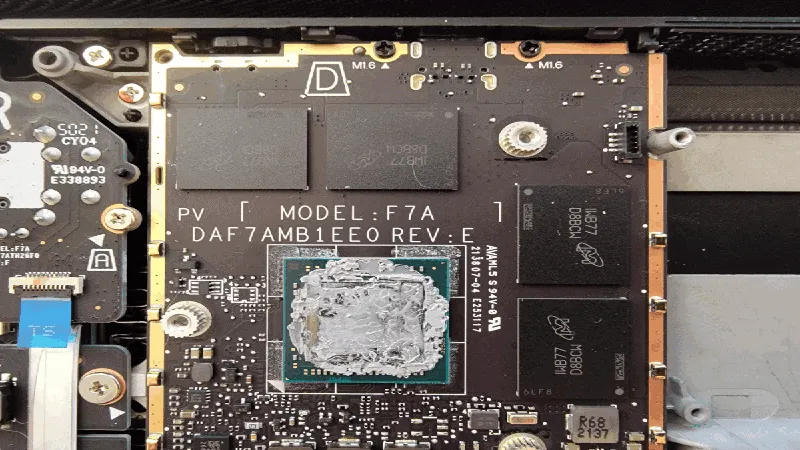
Honeywell is offering one of the world’s leading thermal materials, PTM7950, for both industrial applications and consumer devices. This solid thermal interface material surpasses traditional thermal products like grease and paste, offering exceptional heat management performance.
With conformable, and thermally conductive materials, it adheres effectively to different surfaces, even uneven ones. It fills the air gaps that usually exist between electronic components and heat sinks. Filling these gaps enables quicker and more efficient heat transfer.
PTM7950 keeps temperatures low for optimal performance due to its higher heat conductivity. In high-performance gaming computers where the CPU and GPU typically run very hot, the application of PTM7950 helps across typical operating temperature ranges.
Even in automobiles, thermal pads are applied to power inverters as they have passed the automotive standard vibration test. These thermal pads provide reliable thermal performance without breaking or sliding under extreme conditions.
Key Features of PTM7950

Why is PTM7950 the best choice for various applications? Have a look at its specifications, making it the best among other thermal adhesives:
| Phase Change Material | PTM7950 |
|---|---|
| Thermal Impedance | 0.04 - 0.08 (°C cm²/w) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 8.5 (w/mk) |
| Specific Gravity | 2.8 (g/cm³) |
| Dielectric Strength | 0.55 kV/mm |
| Volume Resistivity | 2.1x1014 Ohms⋅cm |
Phase Change Technology
The PTM7950s exceptional thermal performance comes from its phase change technology. When this material melts into liquid, it takes in as much heat as possible. Once the device shuts down or cools off, the temperature plummets and the material snaps back into solid, releasing all that stored heat in the process. This ongoing back-and-forth cycle helps the CPU stay safe, which in turn keeps it running for a long time.
Lower Thermal Impedance
This is the most effective option in terms of low thermal impedance. Thermal impedance refers to the resistance against heat flow. A material with low thermal impedance lets heat sweep through its surface in no time. This is a remarkable feature of thermal interface material, transferring heat quickly, so your heat sinks can keep temperatures under control.
Higher Thermal Conductivity
Among various materials, PTM7950 is the best choice for thermal conductivity. The higher conductivity is due to the conformable materials. But to make the pad more effective, a thin bondline is necessary for proper application. This is again a specification achievable by the phase change thermal pad.
Lower Bondline Thickness
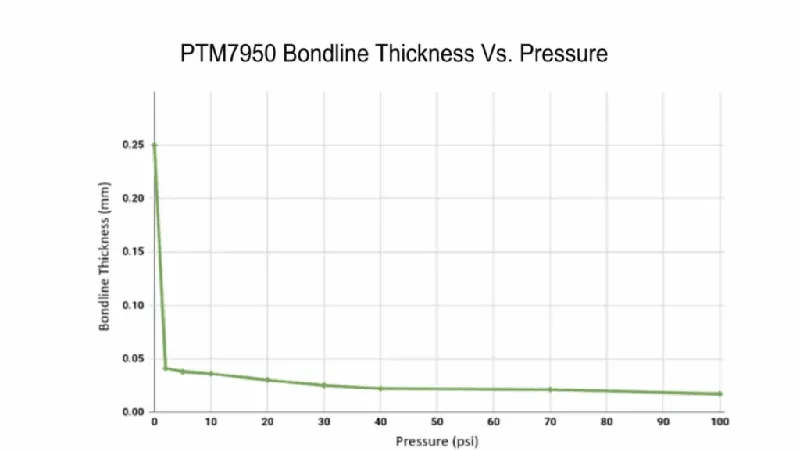
Bondline means the thickness of the phase change material layer as used between the two surfaces, such as the heatsink and the electronic unit. Pressure must be applied during the application of thermal products to get a thin bondline.
With some pressure applied (≥10 psi), the bondline thickness of the thermal pad decreases, resulting in higher thermal conductivity and lower thermal impedance as well.
Excellent Interface Wettability
PTM7950 is easy to apply with better contact between the two surfaces as it has higher interface wettability. Once applied to a computing or other electronic device, this thermal interface material melts upon heating and spreads evenly across the surface, filling air gaps. This is another factor behind its higher thermal conductivity.
Long-Term Reliability
These materials are not only conductive but also safe for use in delicate electronics like LED setups and optical equipment. They don’t contain siloxanes means there’s no risk of outgassing or ruining your system instead the performance will be stable and consistent.
The polymer-based design makes them super reliable as they won’t leak or pump out, even in extreme conditions.
Appropriate Specific Gravity
PTM7950 has an optimal specific gravity, not too high and not too low, which reflects its density. A higher specific gravity means the thermal material is denser compared to water. Having the right density is essential for both performance and ease of application. If a material is too dense, it becomes difficult to melt and spread onto the surface of heat-generating components.
Furthermore, an appropriate density allows for better heat transfer due to the presence of high thermal conductivity fillers. It enables smooth coverage between the electronic unit and the heat sink, ensuring effective heat dissipation.
Wider Range of Application
Among various thermal interface materials, PTM 7950 comes with the highest heat conductivity, making it suitable for automotive and power applications, LED lighting, high-performance gaming consoles and PCs. For electronic devices and machines that operate under intense conditions and heat up too quickly, these phase-change thermal pads work best.
Availability of Variables
Other than the pad, this thermal interface material is also available in the form of paste, known as PTM7900-SP and PTM7950-SPS. As compared to the pad, these pastes required more time to dry after application, as they are more viscous due to the presence of the extra solvent. That is why pastes are more preferred for screen or stencil printing. Apart from this, these pastes share the same characteristics, offering lower thermal impedance and excellent performance.
What is Thermal Paste and Its Use?

Just like a thermal pad, thermal paste is used to transfer heat between electronic units and their heat sinks. Its application prevents overheating and improves the longevity of different computing components. Due to its greasy texture, it fills air gaps between surfaces to support quick heat flow toward the heat sink, helping keep temperatures low.
PTM 7950 vs. Thermal Paste: Which one Is Better?
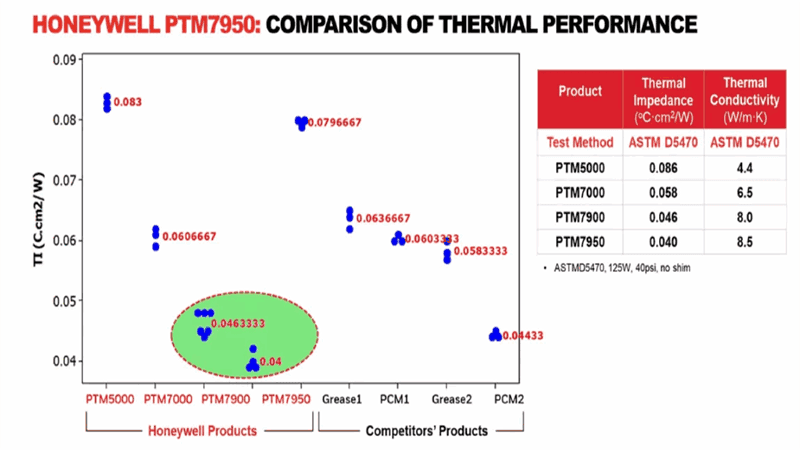
Both thermal pads and thermal paste are useful for heat emission. Understanding their specifications will help you make an informed decision. Have a look at the differences between these two thermal interface materials:
Ease of Application
Thermal paste with lower specific gravity is less dense than pads, making it easier to apply on a wide range of applications. On the other hand, pads have a higher specific gravity; customers may find it difficult to apply them to the CPU and GPU.
Higher Prices
In terms of competitive cost, thermal paste is more affordable than thermal pads. Phase change thermal pads are generally more expensive than other thermal materials.
However, being highly durable, their costs will skyrocket. You don’t have to reapply them frequently as they keep their properties and heat-conductivities on track over time.
Durability
In terms of durability and long-term heat conductivity, thermal interface materials like PTM7950 are superior to traditional thermal grease. They don’t dry out over time, which is the case with thermal pastes. The material slightly melts when heated or when the device is in operation, and then solidifies again as it cools. These self-regulating properties prevent any risk of leakage or spillover.
Thermal Impedance
As compared to competitive thermal greases, PTM7950 have lower thermal impedance values, making it suitable for various devices for exceptional thermal management. Right after its application, the customer noticed a huge drop in the temperature of the CPU, GPU, and other heat producing parts.
No Regular Maintenance
Thermal pads work well under a wide range of conditions without drying out or losing their grip.
On the other hand thermal paste can dry out over time, which means you’ll be keeping a check for reapplication whenever the temperature escalates, fans getting louder, or the performance is slowing down.
Which Thermal Solution is Best for Use?

There is no hard and fast strict rule for choosing the best option. Both phase change materials and thermal grease have their pros and cons. The final choice depends on your application and usage. Here are a few things that help you go for the best one:
- If you are looking for budget friendly options, thermal grease is highly recommended.
- If you want a low maintenance thermal solution, thermal pads are the right choice.
- Thermal paste comes with potential application errors, as applying too much or too little reduces overall performance. This is not the issue with the phase change thermal pad. You just cut and paste it on the heat-producing surface
- Moreover, if you want to fill larger gaps, then thermal pads are better to use. On the other hand, thermal grease is best for small gap filling.
- If there is a risk of short circuits around sensitive electronic components, then a silicone-free thermal pad is the best option. You also don’t have to worry about siloxane contamination.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is the thermal pad design essential for thermal conductivity?
Yes, an appropriate thermal pad design ensures complete filling of air gaps between surfaces for effective heat transfer. The conformable structure makes pads suitable for irregular surfaces. Upon heating, the phase change pad becomes extra soft, leading to effective heat transfer and scalable application.
What are the different types of phase change material available in the market?
Different phase change material are available in the market such as:
- PTM7900-SP
- PTM7950
- PTM6880
- PTM7000-SPM
- PTM6000
- PTM6000-SP
- PTM6000HV-SP
- PTM5000, etc.
Is PTM7950 suitable for high-end computing devices?
Yes, the higher thermal conductivity and low heat impedance make this thermal material effective for computing components, including gaming consoles. You can apply it directly to the CPU, SSD, circuit chips and GPU.
Can I use PTM7950 for an automotive component for heat dissipation?
Yes, this top-notch thermal interface material works well for automotive components. It stays solid and transfers heat efficiently in high temperatures, pressure and other harsh conditions.
What are the available thicknesses for PTM7950?
This thermal interface material is available in various thicknesses (mm), so you can select according to the surface flatness:
- 0.2
- 0.25
- 0.3
- 0.4
- 0.5
What is the shelf life of PTM7950?
The shelf life of this phase-change thermal pad is around 12 months.
How can I achieve the minimum bondline thickness of the PTM7950?
You can achieve the minimum bondline ideal for higher thermal conductivity by applying a clamping pressure of around 30 psi at 60°C for 30 minutes. This way, you can achieve lower thermal impedance as well.
Do world-leading computing and other electronic brands prefer PTM7950?
Yes, you can see widespread use of PTM7950 by well-known brands such as:
- Nvidia
- Intel
- AMD
- Meta
- Apple
- Cisco,
- IBM,
- HSBC, etc.
Bottom Line
PTM7950 is one of the most reliable thermal interface solutions thanks to its novel polymer PCM system. You can see its widespread use in high-end electronic devices due to its exceptional thermal conductivity. With a thin bond line, it keeps the temperature within a normal range.
Its lower thermal impedance improves performance and life span of computing units, LED lighting, automotive and industrial devices, etc. Moreover, with greater reliability and heat-conductivity than thermal grease, PTM7950 is the best choice.