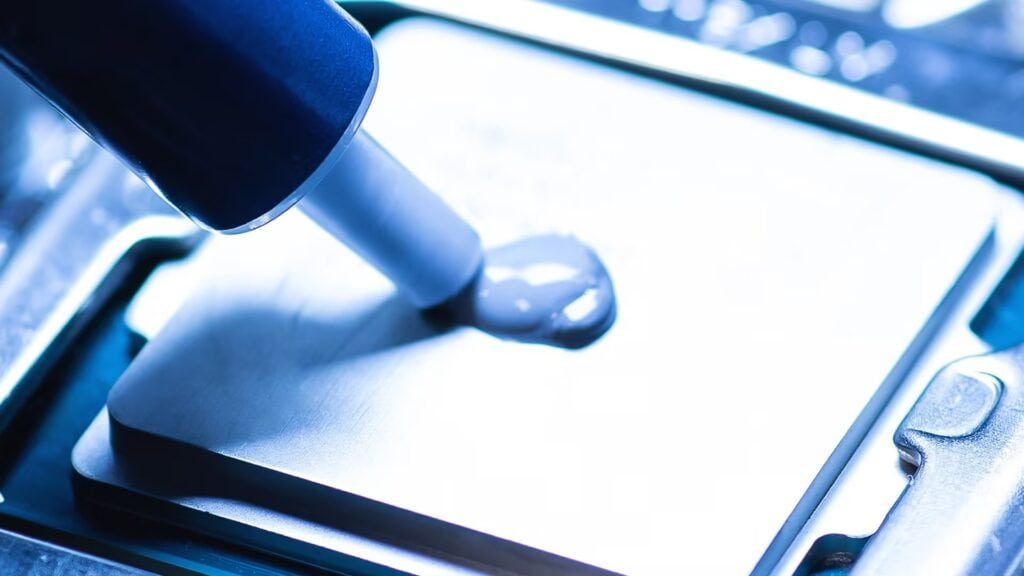
Relentless innovation due to growing demand for sustainable modes of transportation in the automotive industry has led to the creation of batteries with exceptional high mechanical strength. In the high-risk world of electric vehicle (EV) battery assembly, effective thermal management is a critical pillar for vehicle safety that cannot be compromised on.
Efficiently balancing charging speed, long-term battery performance, and thermal propagation is a major challenge faced by automotive manufacturers. One of the most damaging factors in balancing that equation is the presence of air pockets in EV batteries.
What Are Air Gaps?
Air gaps are microscopic and macroscopic voids found in battery components, a primary cause of increased resistance to the heat generated within EV battery packs. Air gaps impact temperature uniformity to a significant extent, reducing heat dissipation and thermal conductivity, especially under the challenging conditions of rapid charging and high-load usage.
In this definitive guide, we will be explaining why and how the empty spaces in EV batteries originate, how they critically impact thermal conductivity, battery performance, and what specific materials (gap fillers) can be used to tackle them.
Why Do EV Battery Air Gaps Form in a Battery Module Assembly?

In electric vehicles, gaps in batteries are not a sign of poor build quality, they are an unavoidable physical phenomenon that arises as a result of a combination of mechanical assembly tolerances, material properties and operational pressure. Understanding how air gaps come about is the first step towards developing a solution to solve the challenge.
Several causes can be responsible for the formation of these gaps which act as insulators. The formation of air gaps usually happens during the design or assembly of a battery pack. In this section, we take a look at some possible reasons why EV battery air gaps form in battery assembly.
Dimensional Tolerances in Cells and Components
No two components are perfectly identical. Each component of a EV battery pack design, from the individual cells to the aluminum cooling plate, are distinctively unique, manufactured to meet a certain tolerance levels and specific sizes.
- Cell Dimension Variations: From cell to cell, lithium-ion battery cells, whether cylindrical, prismatic, or pouch-shaped, exhibit slight variations in height, width, and thickness. A prismatic cell with a height of 90 mm might actually be 90.05 mm high, while the one next to it is 89.95 mm high.
- Cold Plate Machining Tolerances: The heatsink at the base of the EV battery also has its own specific flatness and machining tolerances. A larger plate may come with slightly deformed surfaces or deviations, leading to gaps or vacuums.
- Stack-Up Tolerance Accumulation: When you stack tens or hundreds components together, these tiny individual tolerances build up. This “stacking tolerance” can result in significant, unpredictable gaps between the bottom of some battery cells and the cooling plate, creating an uneven thermal contact path.
Surface Roughness and Micro-Unevenness
To the ordinary eye, the surface of an EV battery cell may look like it is perfectly smooth. However, when placed under closer microscopic scrutiny, you will find a rough, rugged, irregular surface, characterized by peaks and valleys.
- Microscopic Peaks and Valleys: When two irregular surfaces are pressed against each other, due to the fact that they are not completely flat, they only come into thermal contact at the high elongation points. Therefore, a microscopic valley is created between the peaks of these two surfaces, resulting in a vast network of air-filled cracks.
- Actual Contact Area vs. Geometric Area: The actual physical contact area may be only 1-2% of the geometric surface. The 98-99% area left is nothing but an insulating layer of air, which significantly restricts uniform heat dissipation.
Cell Expansion During Charge–Discharge Cycles
Lithium-ion battery cells are not static objects, they slightly contract and even swell sometimes due to charging and discharging cycles.
- Swelling Leads to Varying Levels of Thermal Contact Pressure: The swelling and contraction that goes on with battery cells is known as volumetric change and it changes the mechanical pressure applied to the thermal interface. As the cell swells, it may press hard against the cooling plate, contraction however, causes it to move apart, creating new or larger air gaps.
- Cyclic Deformation Creates Micro-Gaps: Over time and after more than thousands of cycles, the constant mechanical stress can cause TIMs to degrade. This action brings about the formation of new air pockets that were not present during the initial assembly, leading to an eventual decline in thermal performance.
Assembly Misalignment and Manufacturing Errors
The assembly process itself stands as a major source of air gaps in EV batteries, especially if the production line is a high-volume one. Below are ways that air gaps could form inside EV batteries during assembly:
- Uneven Compression: During assembly, force is usually applied to compress the EV battery module, but sometimes it is not perfectly done to be uniform across the entire module. This would eventually lead to the presence of a closer thermal contact between some areas and wider gaps in others.
- Inconsistent Fixture Pressure: there could be slight variations in applied pressure exhibited by the fasteners used in electric vehicle battery assemblies, creating inconsistencies between the modules.
- Flatness Deviations: Deformation of the EV battery casing or deviations in the flatness of the cooling plate can result in the formation of large, uneven gaps that are particularly difficult to fill.
The Critical Impact of EV Battery Air Gaps on Battery Thermal Performance
The presence of air gaps and empty spaces in EV batteries is not a minor inconvenience; it is a critical flaw in the battery design which will eventually have direct impacts on user safety and the longevity and performance of the electric vehicle battery pack. Air is an excellent thermal insulator, the direct opposite of what a proper thermal management system needs.
So how do air gaps in EV batteries impact the high thermal conductivity of the battery?
Increased Thermal Resistance
This is a measure of how difficult it is to transfer heat through a material. Air has an extremely low thermal conductivity, just around 0.025 W/m K. In contrast, a typical thermally conductive gap filler may have a conductivity of 3.0 to 8.0 W/m·K, sometimes even more. An air gap is a thermal barrier, as it traps heat inside the battery cells and prevents heat transfer from the heat source towards the active cooling system.
Temperature Non-Uniformity (ΔT > 5–10°C)
The most damaging impact that air gaps have on EV batteries is temperature inconsistency across the battery pack. A cell placed over a large air gap will become much hotter than a cell with good thermal placement, resulting in dangerous hot spots. It is not uncommon for batteries to degrade more rapidly at high temperatures. A temperature difference (ΔT) of more than 5°C between cells can cause the hotter cells to age faster and lose their capacity.
Reduced Fast-Charging Efficiency
Fast charging generates an incredible amount of heat in a short period of time. The Battery Management System (BMS) carefully monitors the temperature of the cell, restricting the charging current if it increases too rapidly. If the heat cannot be removed in time due to the insulating effect of the air gaps, the BMS will limit the charging rate. It does this so as to avoid overheating, and this results in longer, more frustrating charging times for the EV owner.
Safety Risks at High Loads and Potential for Thermal Runaway
This is the most critical impact. At high discharge rates (for example, during rapid acceleration), hot spots caused by empty spaces in electric vehicle batteries can push a cell’s temperature toward a safe limit. If a single cell overheats and enters a thermal runaway situation, the tremendous amount of heat generated can cause cascading failures in nearby cells.
Engineering Solutions to Eliminate EV Battery Air Gaps
To address air gap challenges in EV batteries, a multifaceted approach that combines intelligent mechanical design with advanced materials science, is required. Below are some design and engineering solutions that you can take as an EV manufacturer or project manager to eliminate air gaps and improve thermal propagation.
Improve Structural Design and Manufacturing Tolerances
The first line of defense to put is the minimization of gaps from the very beginning. This can be achieved by improving on machining accuracy of the cooling plates, design of the devices (to give more uniform tightening), and rigorous control of stacking tolerance. However, it is incredibly expensive to try to achieve near-perfect tolerances levels, especially for high-volume automotive production.
Optimize the Compression Strategy
It is crucial that you apply uniform clamping pressure across the entire EV battery pack. With the aid of smart designed compression frames and ensuring assembly pressure constant, it is possible to reduce the size of the gaps caused by production variations. Doing this, however, does not completely eliminate microscopic gaps. If not, what then is the most reliable solution?
Apply Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs)
The application of TIMs is, without any doubts, the most effective and practical solution. By applying a thermally conductive material in the air gaps of your EV battery, the insulating air is replaced with a conductive path, preventing overheating. These thermal interface materials are specially designed to conform to surface irregularities and ensure that there remains a continuous path for heat flow from the battery cells to the heat sink. The most common types used in EV applications include:
- Thermal Pads
- Thermal Gels (Gap Fillers)
- Thermal Greases
- Thermal Putties (Thermally Conductive Gap Fillers)
TIM Material Solutions for Filling Air Gaps in Electric Vehicle (EV) Battery Packs and Improving Battery Performance
While improving design tolerances and optimizing compression strategies can prove to be helpful, the most effective and practical solution is the application of high performance thermal interface materials (TIM). These broad range of materials are specifically designed to conform to surface irregularities and ensure a continuous, seamless heat path from the battery cells to the heat sink.
- Thermal Gap Fillers (Gels and Putties): The Ultimate Conformity
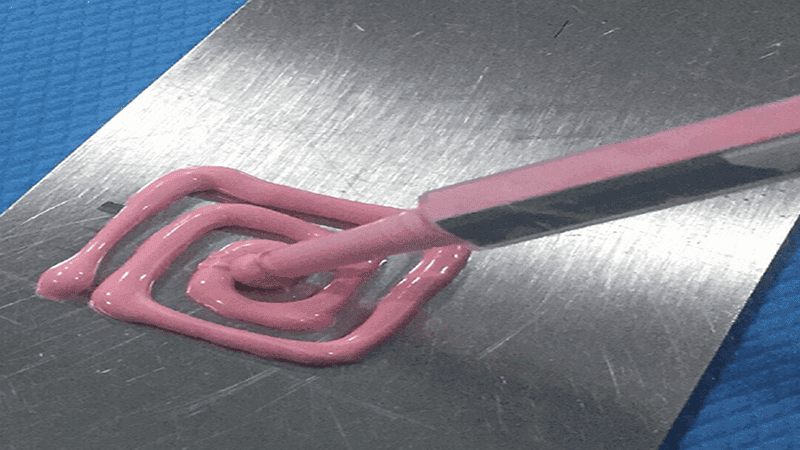
Thermal gap fillers work by flowing into the crevices and conforming before curing into place. Once it has been dispensed at a steady flow rate, this gap filler then eases into every crevice, around every key component, completely filling cracks of various heights and shapes and replacing the insulating air.
During polymerization (at room temperature or with gentle heat), it forms a solid, yet highly conformable, monolithic block of thermally conductive material.
This unmatched conformability is the key to their superior contribution to battery life. By eliminating virtually all air pockets that lead to high temperatures, they create the most efficient and uniform heat transfer path possible. This results in the lowest possible thermal resistance and the most uniform temperature profile across the entire battery module.
JIUJU formulates its high-performance silicone free gap fillers with advanced polymer technology, providing you with excellent vibration dampening and improving thermal contact. This is something other gap fillers may struggle with.
- Thermal Pads: The Solid, Stable Solution
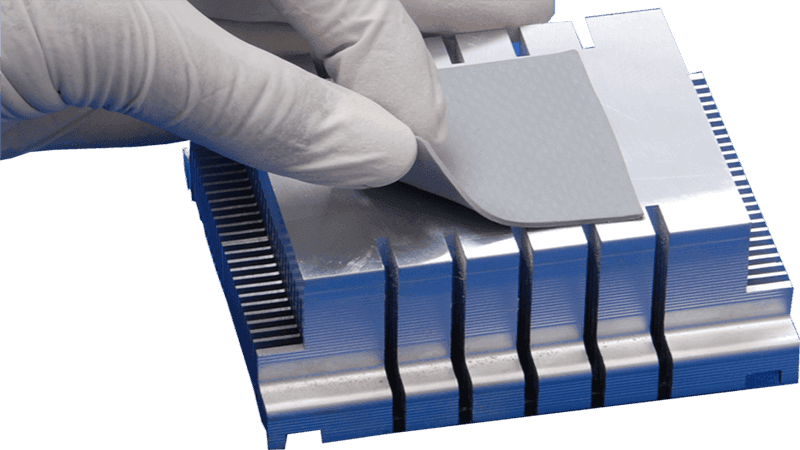
Thermal pads are pre-cured solid sheets of a polymer base (typically silicone) that have been filled to a great extent with thermally conductive ceramic particles. They are made with precise thicknesses and can be die-cut into any shape.
Thermal pads work by compression. When the EV battery is assembled, mechanical pressure is applied, thereby causing the pad between the battery cells and the cooling plate to be compressed.
The inherent softness and flexibility of the thermal pad makes it possible for it to deform slightly, covering surfaces and filling both microscopic surface vacuums and small uniform macroscopic spaces.
A well-chosen thermal pad is a key factor in preserving the vehicle’s driving range throughout its lifespan. They are perfect for fast paced assembly lines, offering excellent dimensional stability and electrical insulation.
- Thermal Grease: The Micro-Gap Specialist
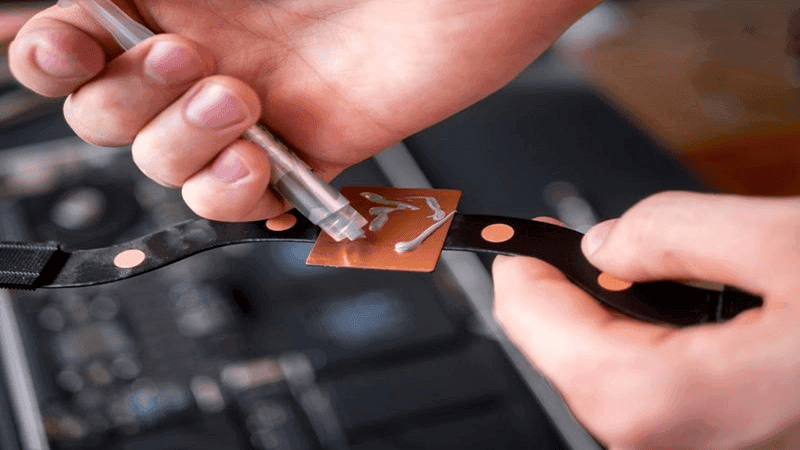

Thermal paste is a non-polymerizing suspension of conductive ceramic particles in a fluid silicone or non-silicone base. Throughout its functional lifespan, this thermally conductive adhesive maintains a paste-like state. While thermal paste is not designed to fill large, macroscopic gaps, it effectively spreads into an incredibly thin bond line when placed between two very flat, smooth surfaces under high clamping pressure.
In the right application (like a CPU heatsink), thermal grease can significantly reduce thermal resistance and extend the life of components. In a more high-vibration environment, like in automotive, the non-polymerizing nature of EV batteries puts it at a significant disadvantage.
- Hybrid TIMs: The Best of Both Worlds
Hybrid thermal interface materials are an innovative class of materials that convolute the strengths of pads and fillers to offer maximum heat management. These classes typically consist of a structural backbone like a fiberglass-reinforced pad, which is then covered with a soft, highly flexible thermal putty or gel.
This dual-action approach allows the soft, flexible material to flow and seamlessly fill large, irregular gaps, just like a traditional filler would. At the same time, the internal structured layer ensures solid mechanical stability and prevents the material from leaking or leaking under pressure and vibration.
Case Studies: Solving Real-World EV Applications Thermal Challenges
The true capability of a TIM is registered in the performance it offers in the field. Here’s how choosing the right solution has solved critical problems for electric vehicle manufacturers.
Case Study 1: Fast-Charging Hotspots Resolved by JIUJU Gap Fillers
An ambitious, innovative EV startup was developing a new battery pack with fast charging being their priority. In the process of carrying out validation tests, the startup discovered a serious problem: the temperature difference (ΔT) between the hottest and coldest cells in a battery module reached 8°C.
This forced the BMS to limit charging. In the analysis provided after, it was revealed that manufacturing tolerances created variable air gaps in electric vehicle batteries of up to 1.5 mm.
After consulting with engineers from JIUJU, they were able to select one of our thermally conductive gap fillers with a good thermal conductivity of 5.0 W/m·K. Using robotic dispensing equipment, the two-component geld was applied to the cooling plate before assembling the module. The result was revolutionary.
The highly flexible gel perfectly filled every space, regardless of size. In the next phase of testing, the maximum ΔT was reduced to just 3°C. This allowed the company to achieve its fast-charging goals and improve the expected lifespan of the battery pack.
Case Study 2: Long-Term Reliability Achieved with JIUJU Hybrid TIMs
A major tier-one automotive supplier with supply chains across the world happened to experience field failures in an off-road electric vehicle application.
Extreme vibrations caused a standard thermal putty to leak between the battery cells and the heat sink over thousands of cycles. This led to a gradual increase in cell temperatures and subsequent pack failure.
This supplier needed a solution that had the conformity of a stucco but the stability of a pad. JIUJU provided one of our advanced hybrid systems. The material’s unique structure ensured solid resistance to emptying, while the soft, flexible layers perfectly filled uneven surfaces.
The new battery module design passed an aggressive 2,000-cycle vibration and thermal shock test with no degradation in thermal performance, ensuring the long-term reliability required for the demanding application.
Conclusion
Air gaps in electric vehicle batteries are a near inevitable consequence of real-world production. These gaps pose a silent threat to performance, security, and battery life. While mechanical design solutions and improvements can help, the most effective, reliable solution to prevent overheating is the proper application of advanced thermal interface materials.
As an automotive manufacturer or engineer, are you going to let air gaps between EV batteries compromise your project? Partner with a world-renowned manufacturer of thermal management components and general cooling systems that understands the science of heat transfer and can provide you with the material solutions you need.
Reach out to our team of thermal interface materials experts today to enjoy each one of the following:
- Customized solutions for EV manufacturers
- Complimentary thermal interface material selection guide.
- A comparative performance report for our latest gap fillers.
- Priority samples for your gap-filling evaluation.