When you think about heat dissipation in electronic devices, it is not unusual that what first comes to your mind is thermal pads for CPUs or thermal pads for GPUs. That’s not strange, considering how power-hungry and arguably hit they can be. However, the electronic component that usually puts the most work on thermal pads is the memory chip.
In this article, you will learn about the different types of memory chips, the heat challenges they face, and how to tackle them using the appropriate TIMs.
The Main Types of Memory Chips
What are the most commonly used types of memory chips? Let’s take a look at the details below.
- DRAM (Dynamic Random-Access Memory)
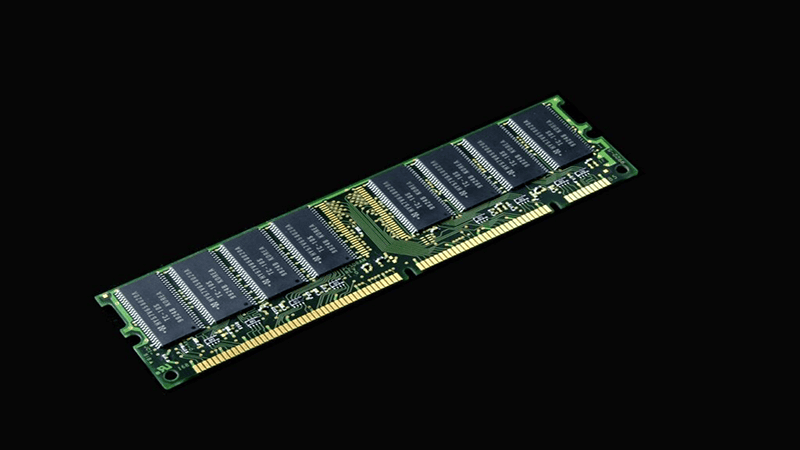
DRAM stands for Dynamic Random-Access Memory. It is the most common form of RAM found in modern computers, workstations, and servers. DRAM chips are composed of millions of single-transistor memory cells. Each cell uses a tiny capacitor to store a single bit of data (a 1 or a 0) in an addressable row-and-column format.
However, capacitors are like leaky buckets; they cannot hold an electrical charge for too long. For this reason, DRAM memory chips require a near-constant electrical current pulse, a process known as REFRESH, to retain the stored information. If a DRAM memory chip isn’t refreshed hundreds of times per second, the data simply disappears.
- The Problem:
As essential as DRAM is, it faces a significant challenge: heat. RAM works by rapidly switching electronic signals, moving data through its chips at incredible speeds. This constant activity is an energy-intensive process, and as memory speed and density increase, so does the heat produced.
The primary source of heat in DRAM is the electrical current required to operate the unit. Higher data transfer rates require higher switching frequencies in memory chips, which directly translates into more electrical current and, consequently, greater heat generation.
Furthermore, the aesthetic RGB lighting that is integrated into your electronic devices comes at a thermal cost. The dazzling LEDs now common on high-performance memory modules may look appealing to the other eyes. Still, each one is a tiny semiconductor that generates heat, especially at high brightness levels.
Eventually, high temperatures can result in a distortion of the delicate electronic signals that represent data. Another effect of heat on DRAM is that it exceeds the safe threshold and can automatically reduce the operating frequency (throttling) under severe thermal stress, slowing down the entire system. This can reduce the lifespan of the memory module.
- The Solution:
This is where Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs) become indispensable. Applying a high-performance TIM, such as those produced by JIUJU, eliminates microscopic insulating air gaps, creating a highly conductive path for heat to escape. For memory applications, thermal paste and thermal pads are the two main solutions, each with specific advantages.
The most suitable TIM and application method depends on the specific build and cooling design of the memory type.
- NAND Flash Memory

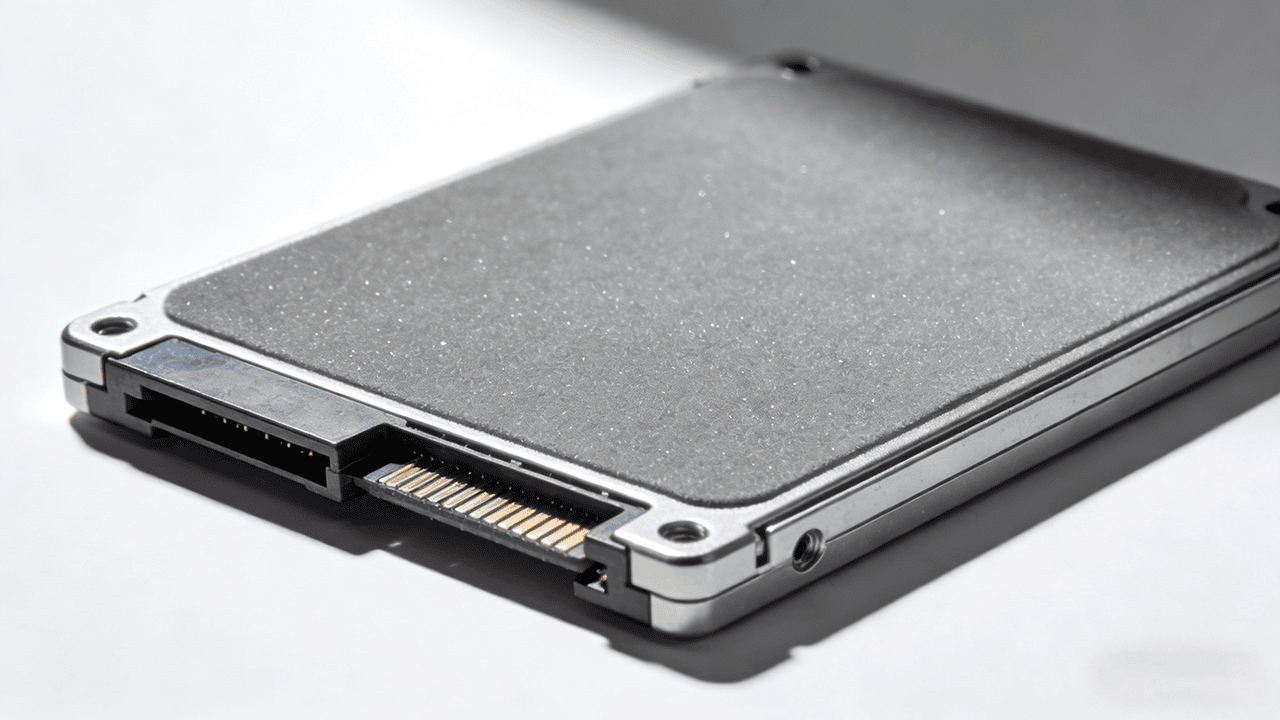
NAND Flash memory is a type of non-volatile storage technology that can retain data even in the absence of power. This durable, high-density memory chip type is the technology behind a wide range of modern devices like USB flash drives, memory cards, and, most importantly, solid-state drives (SSDs).
In an effort to minimize the cost per bit and maximize chip capacity, NAND Flash memory has quickly become the go-to storage solution for computers and other electronic devices. NAND Flash Memory excels specifically in scenarios where large files are frequently saved, read, and deleted.
Typically, NAND Flash memory uses electrical circuitry to store data in blocks. It uses a component known as a floating-gate transistor (FGT), which operates like a NAND gate, allowing data to be stored and retrieved by trapping or releasing electrons.
- The Problem:
Most consumer NAND Flash memory products are designed to operate within a relatively favorable temperature range, typically between 0°C and 70°C. This is generally alright for devices used in temperature-controlled commercial or consumer applications.
However, if you need NAND Flash memory specifically for an industrial or power-demanding application that involves operating under extreme conditions, be ready to get plagued with high temperatures. For example, flash memory embedded in aircraft or train systems is subjected to both extreme temperatures and rapid temperature fluctuations.
It is important to bear in mind that failures in these industrial devices can be extremely costly and, in some cases, dangerous. For instance, if a medical device, such as a patient monitor, were to fail due to a temperature issue affecting its embedded memory, patients’ health could be immediately put at risk. Similarly, a failure in an avionics or railway control system could create dangerous conditions for passengers.
- The Solution:
The solution to tackling this problem is a high-conductivity thermal pad for SSD. These thermal pads are the universal solution for all SSDs. You can use a single, custom-cut m2 SSD thermal pad from JIUJU to bridge the gap between all hot components on the SSD PCB (NAND chip, controller, DRAM cache) and a metal heatsink.
JIUJU thermal pads are flexible enough to connect with components of slightly different heights. It absorbs heat from all sources simultaneously and transfers it to the heatsink. Due to its ability to effectively transfer heat directly to a device’s metal chassis, it is also an ideal thermal pad for SSDs without a heatsink.
For SSDs, the thickness of the thermal pad is critical. It must be carefully chosen to bridge the gap without placing excessive physical stress on the BGA controller chip’s solder joints.
- HBM (High Bandwidth Memory)
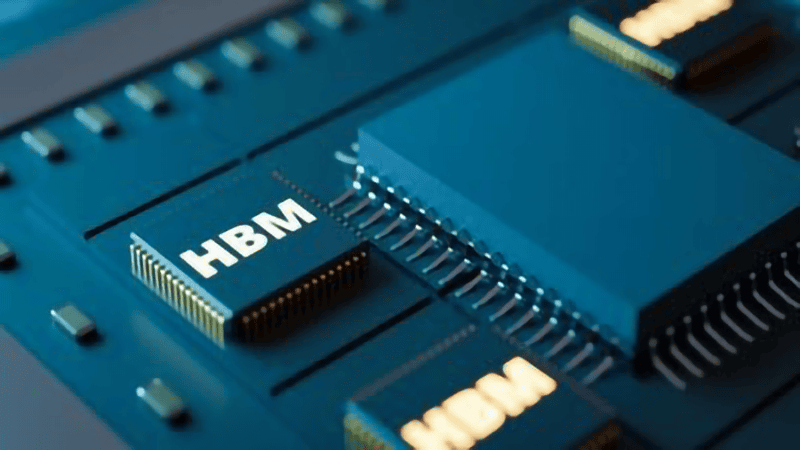
A high-bandwidth memory (HBM) chip is a high-performance, 3D-stacked DRAM designed to solve the memory wall problem that users face when carrying out high-performance computing. The build of this type of memory chip is made up of multiple layers of DRAM chips stacked vertically and connected via TSVs (through-silicon vias).
These 3D stacks are then placed on a silicon interposer, very close to the processor. This proximity helps to reduce the distance data must travel by a significant extent. As a result of this, the speed of data is improved, latency is reduced, and energy efficiency is increased.
HBM memory chips offer enormous parallel data bandwidth, unlike conventional DDR or GDDR, while consuming significantly less power. The build of this chip supports multi-terabyte-per-second throughput, making it a great option for data-intensive applications like AI training, data analytics, high-performance computing (HPC), and advanced graphics rendering.
- The Problem:
The thermal management challenges associated with HBM have become increasingly complex with each new update. The evolution from HBM1 to HBM3E to HBM4 has been characterized by a bandwidth that’s constantly on the increase. As a result of that, more heat is generated within the same confined space.
As the computing demands of data centers, AI applications, and HPC continue to grow, the need for efficient thermal solutions becomes unavoidable.
- The Solution:
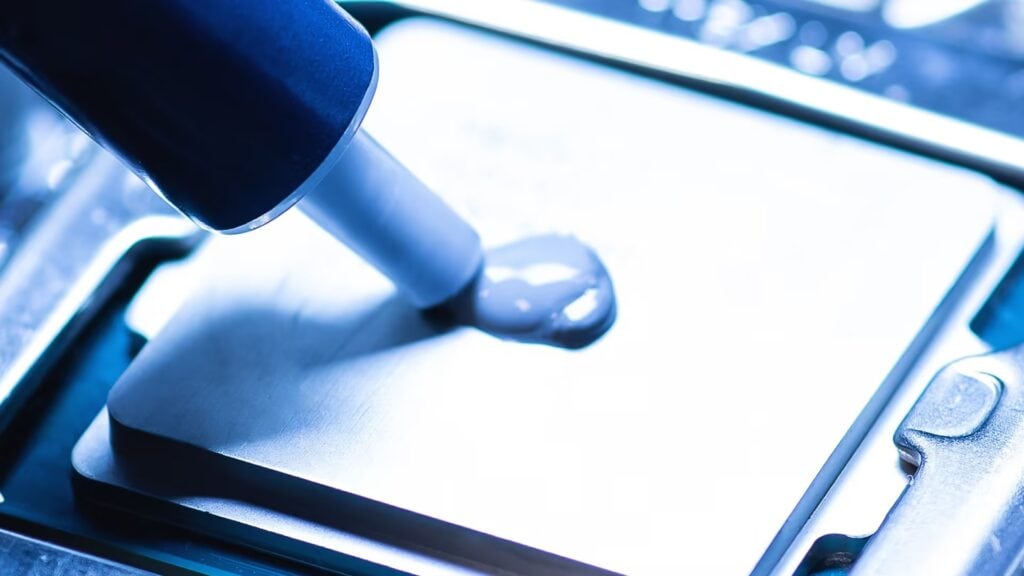
To solve the issue of overheating in HBM chips, you will need high-quality thermal grease– the only viable solution in this scenario. The reason thermal grease is the best option is due to the extremely small and critical interface spaces between the top of the HBM stack, the processor die, and the bottom of the IHS.
You should apply a precisely measured amount of JIUJU’s ultra-high-performance, non-conductive thermal grease to tackle these thermal issues. The grease’s ability to distribute itself in an incredibly thin bond line is essential to minimize thermal resistance in this high-risk environment.
- GDDR (Graphics Memory)
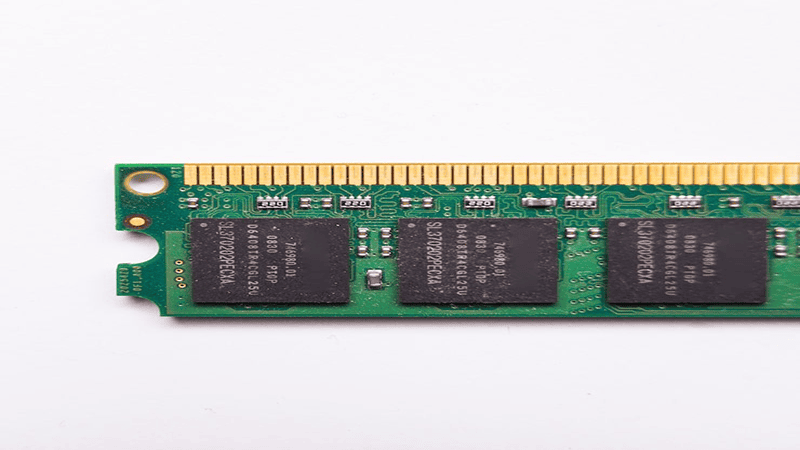
GDDR (Graphics Double Data Rate) is a specialized type of high-performance memory chip built specifically to meet the unique demands of graphics processing. GDDR offers significantly greater memory bandwidth. It is crucial for handling the massive amounts of parallel data required to render high-quality images, complex 3D scenes, and high-resolution videos.
GDDR is primarily found in dedicated graphics cards (GPUs) and other devices where graphics performance is essential, such as gaming consoles.
- The Problem:
GDDR7 is the latest version of GDDR, and it boasts even faster speeds, greater efficiency, and improved features. It is designed to meet the extreme demands of next-generation gaming, artificial intelligence, and high-performance computing, ensuring GPUs can handle the ever-increasing data loads and graphics complexities of the future.
Nonetheless, this leap in performance brings with it a more intense thermal problem, namely, higher operating voltages. To achieve maximum performance, GDDR7 may require slightly higher voltages than its predecessors, which directly contributes to increased temperatures.
Modern HPC and AI systems also often use multiple memory modules in proximity. This adds to the thermal challenges already being faced, as heat from one component can affect nearby components.
- The Solution:
Employ a high-quality thermal pad for GPU memory. For GDDR memory chips, thermal pads are basically the industry standard. The custom-cut pads are precisely positioned on each GDDR chip. They bridge the gap between the memory chips and the heatsink baseplate.
Highly conductive thermal pads are designed to handle the intense heat flow of GDDR6 and GDDR7 memory while providing crucial electrical insulation. For the central GPU die that generates the most heat, you should use thermal grease/paste. Thermal grease provides the most efficient heat transfer to the heatsink.
Why Memory Chips Need Thermal Pads
While using thermal pads for CPU or GPU applications has always been the norm, the need for effective thermal management in memory chips has only become more pronounced in the era of artificial intelligence. According to Professor SangHoon Shin of Hayang University ERICA, who previously worked on Apple’s M1/M2 chip packaging and Tesla’s self-driving AI chips, the efficiency with which heat is dissipated is directly related to the reliability of semiconductors.
Shin, whose primary field of research is advanced semiconductor packaging and full-stack reliability engineering, emphasizes a key rule of thumb: when a chip’s temperature increases by just 10 degrees Celsius, its operating lifespan is effectively halved.
This is why memory chips benefit so much from thermal pads, which include:
- Absorbing mechanical tolerances across multiple components.
- Offers consistent pressure and thermal contact across multiple chips.
- The best thermal pads for SSDs provide electrical isolation of memory chips, with efficient heat conduction.
What Kind of W/mK in Thermal Pads for Memory Chips?
When choosing a thermal pad for memory applications, you don’t always need the highest thermal conductivity (W/m · K) available on the market. The goal is to find the optimal balance between thermal performance and compliance, while considering cost-effectiveness, as we expect that the thermal pad for SSD price is a key factor if you are a high-volume manufacturer.
For memory chips like DDR4, DDR5, GDDR, and NAND Flash Memory, middle-ground W/mK values ranging from 2.0 to 5.0 W/m are arguably the most effective for a standard m2 SSD thermal pad.
Thermal pads in this category aren’t expected to be incredibly structurally durable; they’re expected to be soft and offer good thermal performance at an excellent price.
JIUJU produces a variety of thermal pads ranging from 1-15 W/mK, offering highly competitive prices, performance, excellent compliance, and being specifically designed for high-volume production needs.
Conclusion
As we continue to witness constant increases in memory speeds and densities, the integration of effective thermal management with high-quality thermal pads and thermal grease is now non-negotiable. Inadequate memory chip cooling is a silent threat; it silently degrades the performance of your system and reduces hardware lifespan, long before any catastrophic failure occurs.
Ultimately, premium thermal design isn’t just about cooling the hottest chip on the board; it’s about protecting components that can’t withstand the long-term stress of sustained heat. Partner with JIUJU, a manufacturer that understands these nuances, today, and let’s help you create reliable, high-performance thermal management products ranging from thermal pads for SSD to high-performance thermal grease for HBM.
Why Trust This Guide
This guide is written by the real engineers at Jiu Ju Tech, the same company that has been making thermal interface materials since 2002. We churn out 15 different products each year and have spent years testing no less than 9 different thermal solutions in our lab. The tips and tricks you read here come from our everyday work with the materials, rather than just some theoretical stuff we found on another website.





